AI in Banking: How Indian Banks Are Using Automation to Cut Costs
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly changing the face of the banking industry in India, as it is enabling banks to function smarter while cutting costs substantially. Right from handling customer inquiries to managing back-office operations, Artificial Intelligence is changing the way banks function in a highly competitive market. With increasing operational costs and the need for improved efficiency, Indian banks are increasingly adopting automation solutions. This is not only making banks more productive but also improving customer experience.

AI-Enabled Customer Service: Minimizing Call Center Expenses
Indian banks are now leveraging AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to efficiently manage large volumes of customer interactions with significantly lower costs compared to traditional methods. The AI technology enables instant handling of common customer inquiries like checking account balances, transaction status, blocking credit cards, and branch details, which previously required extensive call center operations. By doing so, banks can minimize personnel expenses related to call center operations while maintaining 24/7 customer service. The latest AI-powered bots are also capable of understanding regional languages and customer sentiments, thus increasing the chances of resolving customer complaints without human intervention. This approach not only helps banks minimize expenses but also reduces customer response times and increases their satisfaction levels. Over a period of time, AI technology continues to learn from customer interactions, thus increasing its accuracy and efficiency. This enables banks to allocate human customer service representatives to deal with complex and high-value customer complaints.
Reducing Costs and Improving Speed through Automation in Back-office Operations
Back-office operations were historically costly and inefficient to operate for most Indian banks. New technologies such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI were introduced in back-office operations to automate tedious tasks like Customer Due Diligence (CDD) for KYC, onboarding customers, data entry, compliance auditing, and reconciliations. RPA and AI solutions reduce the absurd amount of manual processing errors by enabling much faster processing of back-office tasks (KYC verification from days to minutes with AI-based document validation systems). RPA systems also create more reliable compliance with regulations by creating an accurate electronic audit trail. Banks can process more transactions while using fewer staff members than ever before by using technology to eliminate or automate repeatable tasks. Therefore, as banks continue to increase their transactional volumes, they can expect to substantially reduce their administrative costs, as well as increase the accuracy and speed at which they complete back office tasking, through the automation of back-office processing. In this challenging, competitive environment, banks will rely heavily on automation to create revenue-generating growth while maintaining tight control over their operational costs.
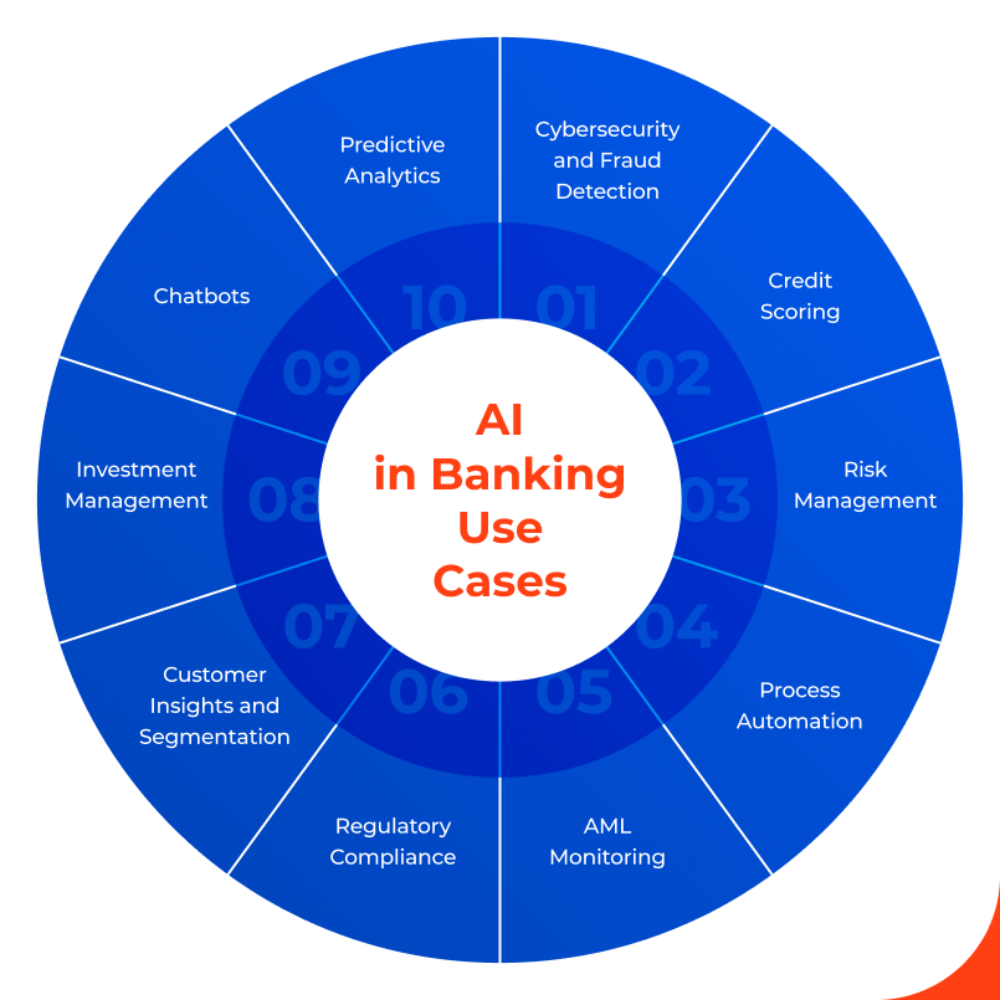
AI in Fraud Detection and Risk Management
Banks in India have significantly benefited from using AI in their efforts to reduce expenses related to fraud detection and risk management. Banks typically use rules-based systems to detect fraudulent activity, but these types of systems are often unable to capture advanced methods of committing fraud (i.e., those that continue to evolve or become more complicated), and they require constant manual inspection by employees. With the use of AI and machine learning (ML), banks can analyze a massive volume of transactions on a continuous basis to identify suspicious behavior (e.g., unusual location or inconsistent usage patterns). By continuing to identify and capture these types of behaviors, banks are able to minimize their losses due to fraud while also reducing the cost associated with performing investigations of fraud after they have already occurred. In addition, banks that implement such systems can make considerable reductions in the size of their fraud monitoring personnel as they will now be able to generate alerts automatically and subsequently be able to prioritize more serious cases. Since machine learning is an evolving technology, banks will continue to benefit over time from improvements made to their fraud detection systems based on the additional data generated from the fraud attempts that have occurred since their implementation. By reducing operational costs as well as minimizing fraud losses, AI-based fraud management results in both cost savings to the bank and enhanced customer trust in the institution.
AI Is Changing How Indian Banks Assess Borrower’s Ability to Repay Loans
Indian banks’ use of AI has significantly changed how banks look at, and ultimately approve, loans for consumers. In the past, manually validating an applicant’s credit history, and whether they could or could not repay their loans, was tedious and time consuming both for the bank, and the consumer. AI models that use relevant, but alternative, data (such as shopping or bill payment patterns etc) allow banks to better determine the likelihood of an applicant being able to repay their loan, while speeding up the loan process, and lowering operational costs associated with obtaining a mortgage or obtaining a line of credit. Banks that improve their ability to assess borrowers’ repayment ability, ultimately decrease their non-performing assets, and that improve banks’ profitability. As a result of reducing defaults, increasing processing efficiencies, and improving overall lender efficiency, banks can offer loans and credit cards to consumers who are un-banked or have not established a credit history, without increasing the associated risk to the lender. Ultimately banks benefit by being able to expand their overall loan portfolio with no additional operating expenses and the credit risk associated with funding un-banked consumers is under control.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a vision for Indian banks in the future—it has already become a necessity. By automating customer service, back-office, fraud analysis, and lending, banks are able to cut down their operational costs to a great extent. AI-based automation not only allows banks to stay ahead in the competition but also helps them to provide better customer service with less staff. As technology advances, banks that make the right investments in AI will be better equipped to handle risks and scale efficiently. In the coming years, automation will be at the forefront of a more agile, cost-efficient, and resilient Indian banking system.